Financial and Compliance Audit of the Department of Human Services
Posted on Apr 11, 2024 in Summary|
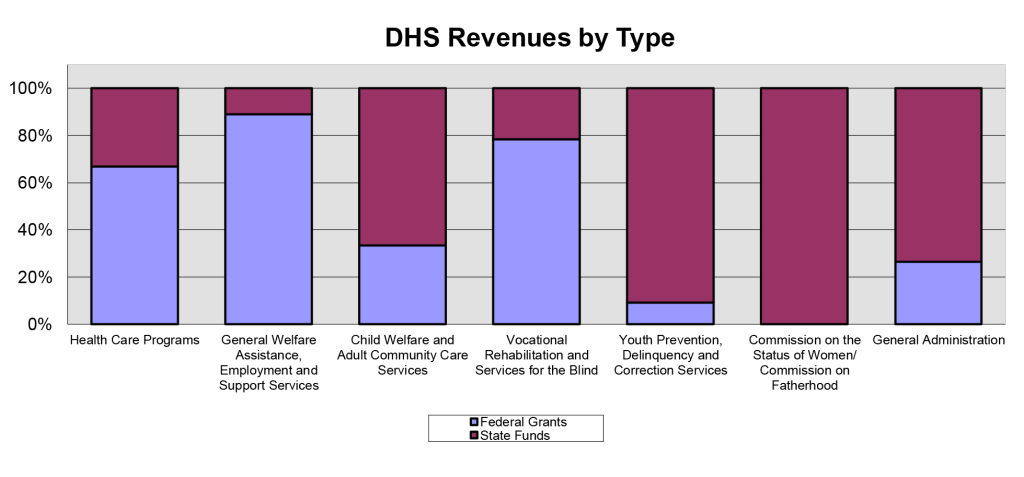
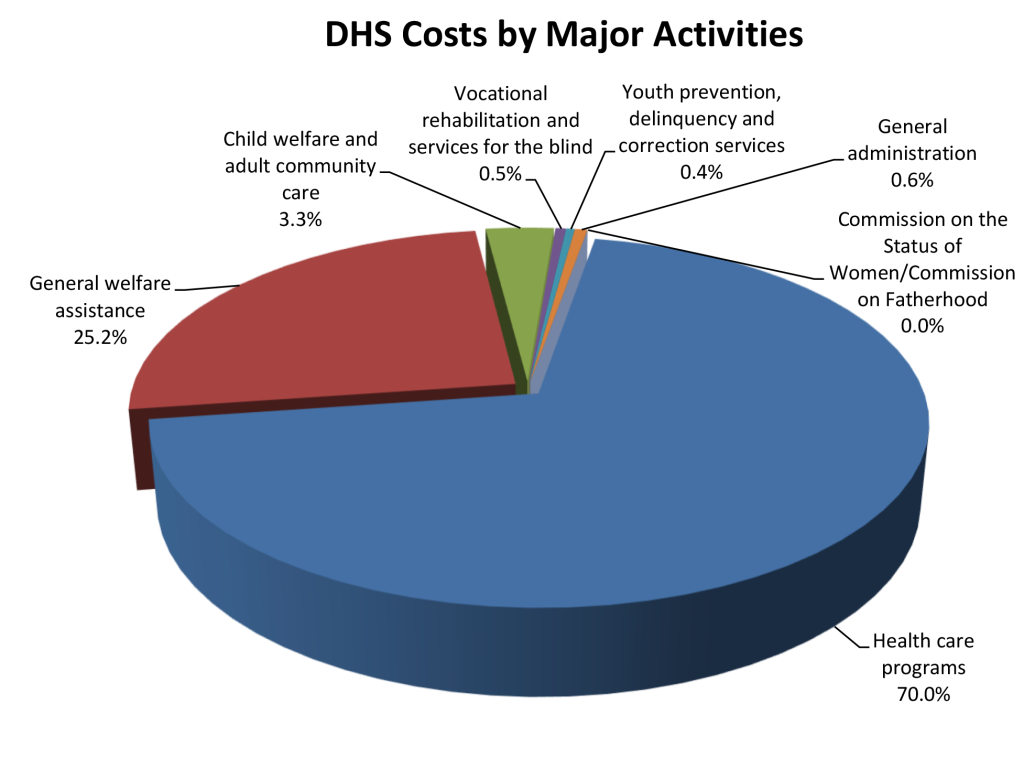
AUDITOR’S SUMMARY Financial Statements, Fiscal Year Ended June 30, 2023 THE PRIMARY PURPOSE of the audit was to form an opinion on the fairness of the presentation of the financial statements for the Department of Human Services, as of and for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2023, and to comply with Title 2, U.S. Code of Federal Regulations, Part 200, Uniform Administrative Requirements, Cost Principles, and Audit Requirements for Federal Awards (Uniform Guidance), which established audit requirements for state and local governmental units that receive federal awards. The audit was conducted by Accuity LLP. Financial Highlights FOR THE FISCAL YEAR ended June 30, 2023, DHS reported total revenues of $5.23 billion and total expenses of $5.14 billion. Revenues consisted of $1.54 billion in state allotments, net of lapsed amounts plus non-imposed employee fringe benefits, and $3.7 billion in operating grants from the federal government. Revenues from these federal grants paid for 71.9 percent of the cost of DHS’ activities. Health care and general welfare assistance programs comprised 70 and 25.2 percent, respectively, of the total cost. The following chart presents each major activity as a percentage of the total cost of all DHS activities. As of June 30, 2023, DHS’ total assets of $538 million included (1) cash of $344 million, (2) receivables of $112 million, and (3) net capital assets of $82 million. Total liabilities of $320 million included (1) vouchers payable of $10 million, (2) accrued wages and employee benefits of $11 million, (3) amounts due to the State General Fund of $57 million, (4) amounts due to other governments of $148 million, (5) accrued medical assistance payable of $77 million, and (6) accrued compensated absences of $16 million. Auditors’ Opinions Findings A material weakness is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control, such that there is reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the entity’s financial statements will not be prevented, or detected and corrected, on a timely basis. The material weakness is described on pages 60-61 of the report. A significant deficiency is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control that is less severe than a material weakness, yet important enough to merit attention by those charged with governance. The significant deficiency is described on pages 62-63 of the report. There were 10 material weaknesses in internal control over compliance that were required to be reported in accordance with the Uniform Guidance. A material weakness in internal control over compliance is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over compliance, such that there is a reasonable possibility that material noncompliance with a type of compliance requirement of a federal program will not be prevented, or detected and corrected, on a timely basis. The material weaknesses are described on pages 65-67, 70-78, and 81-82 of the report. There were five significant deficiencies in internal control over compliance that were required to be reported in accordance with the Uniform Guidance. A significant deficiency in internal control over compliance is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over compliance with a type of compliance requirement of a federal program that is less severe than a material weakness in internal control over compliance, yet important enough to merit attention by those charged with governance. The deficiencies are described on pages 64, 68-69, 79-80, and 83 of the report. |
| About the Department
The Department of Human Services (DHS) works to provide benefits and services to individuals and families in need. The majority of DHS’ budget is comprised of federal funds. DHS’ mission is to direct its funds toward protecting and helping those least able to care for themselves and to provide services designed toward achieving self-sufficiency for clients as quickly as possible. Activities include health care programs; general welfare assistance, employment and support services; child welfare and adult community care services; vocational rehabilitation and services for the blind; youth prevention, delinquency and correction services; and general administration. Attached programs include the Commission on the Status of Women and the Commission on Fatherhood. |