Financial Audit of the Public Utilities Commission
Posted on May 20, 2021 in Summary|
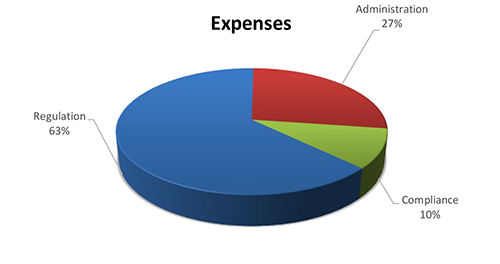
AUDITOR’S SUMMARY Financial Audit of the Public Utilities Commission THE PRIMARY PURPOSE of the audit was to form an opinion on the fairness of the presentation of the financial statements for the Public Utilities Commission, as of and for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2020. The audit was conducted by Accuity LLP. Financial Highlights FOR THE FISCAL YEAR ended June 30,2020, the PUC reported total revenues of $19.4 million, along with $5 million in transfers from other state departments, and total expenses of $11.3 million. Revenues consisted entirely of program service fees. Revenues were offset by $7.6 million in transfers and lapses of State-allotted appropriations, resulting in a change in net position of $500,000. Total expenses of $11.3 million consisted of $7.1 million for regulation, $3 million for administration, and $1.2 million for compliance.
As of June 30, 2020, total assets of $25.4 million exceeded total liabilities of $1.5 million, resulting in a net position of $23.9 million. Total assets included (1) cash of $6 million, (2) fees receivable of $9.4 million, (3) net capital assets of $9.2 million, and (4) other assets of $800,000. Auditors’ Opinion THE PUC RECEIVED AN UNMODIFIED OPINION that its financial statements were presented fairly, in all material respects, in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. Findings THERE WERE NO MATERIAL WEAKNESSES in internal controls over financial reporting that were required to be reported under Government Auditing Standards. However, the auditors identified two significant deficiencies in internal control over financial reporting. A significant deficiency is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control that is less severe than a material weakness, yet important enough to merit attention by those charged with governance. The deficiency is described on pages 42-43 of the report. |
| About the Department
The Public Utilities Commission (PUC) was established in 1913 by Act 89. Its primary duty is to protect the public interest by overseeing and regulating public utilities to ensure that they provide reliable service at just and reasonable rates. The PUC regulates all chartered, franchised, certificated, and registered public utility companies operating in the State of Hawai‘i. It also reviews and approves rates, tariffs, charges and fees; determines the allowable rate of earnings in establishing rates; issues guidelines concerning the general management of franchised or certificated utility businesses; and acts on requests for the acquisition, sale, disposition or other exchange of utility properties, including mergers and consolidations. The PUC is composed of three commissioners appointed by the Governor for staggered four-year terms. The PUC is placed within the Department of Commerce and Consumer Affairs for administrative purposes. |